CANSATS (2017 & 2018)
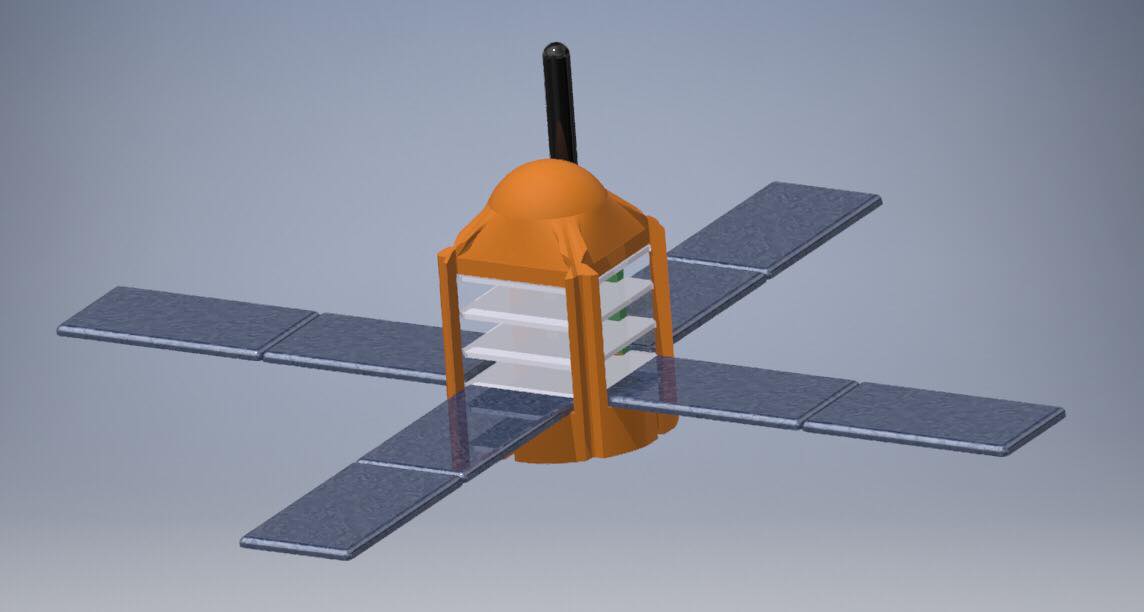
Description
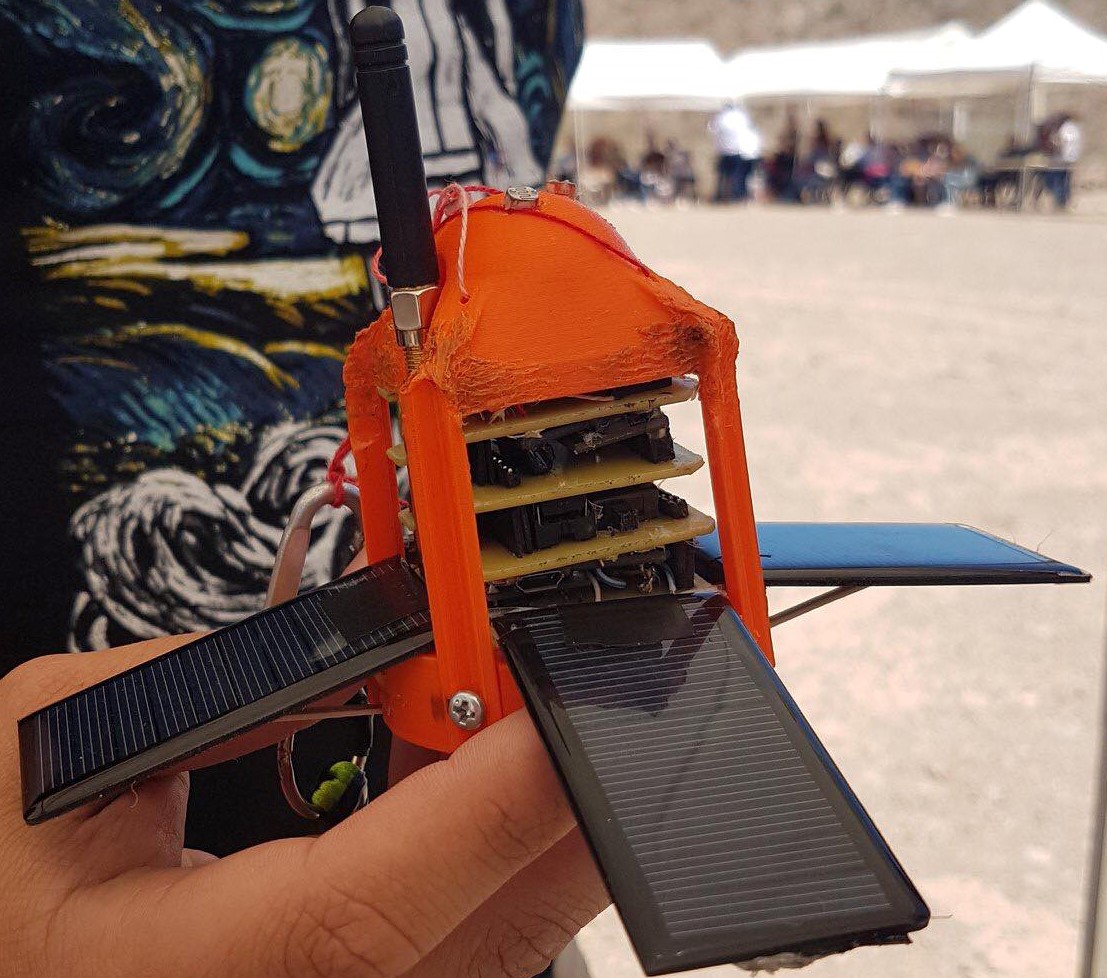
The CanSat competition is an annual state competition in which university students develop CanSats, consisting of can-sized satellites that fulfill a mission (defined by the team) and must be validated with data acquired by the satellite. The CanSats are launched via a model rocket.
The purpose of our CanSat is to do a long-term survey on terrain and its effectiveness for so solar panel development. This was achieved by monitoring the daylight time in each day (if it’s on another planet) and the solar radiation. The CanSat can be sustainable with the solar panels that are extended.
My contribution
PCB Design
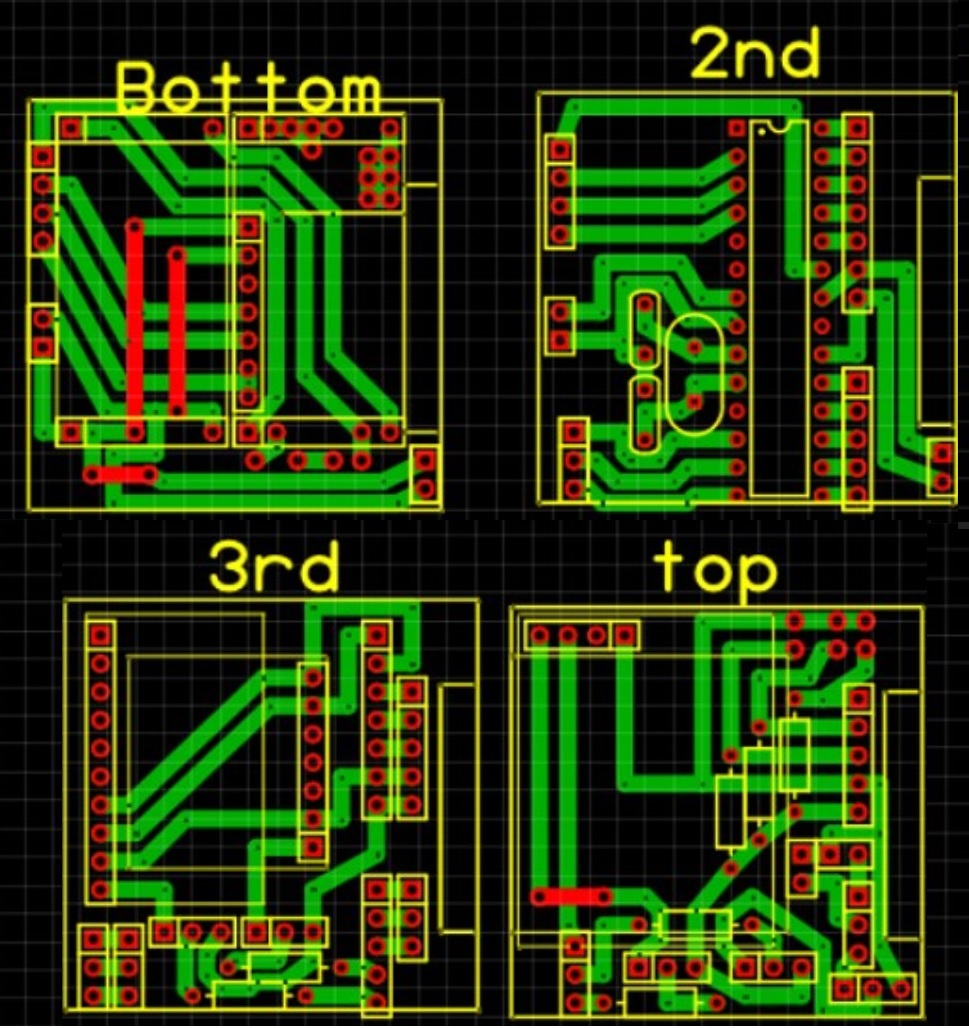
The development of the PCB design considering the small space available, and resources that were available. The design was created with multiple "stacks" of circuits to minimize the space used and allow for multiple through hole components to fit in place. The circuit consisted of single sided PCB boards that are handmade and etched using Ferric Chloride solution, where each stack has different purposes from power distribution and regulation (1st layer), Microcontroller module (2nd layer), IMU and altitude sensor (3rd layer) and GPS and light sensors (4th layer).
Telemetry and Sensor Data
Worked on the interpretation of data for all the sensors on-board which include GPS, IMU, Barometer, solar panel voltages and currents, and light intensity sensors, this was processed and interpreted by the on-board microcontroller. The telemetry was achieved via LoRA communication providing a distance of 4 km range while there is line of sight, and packets of information were sent with a CSV format and a low data with 300 bytes per packet.
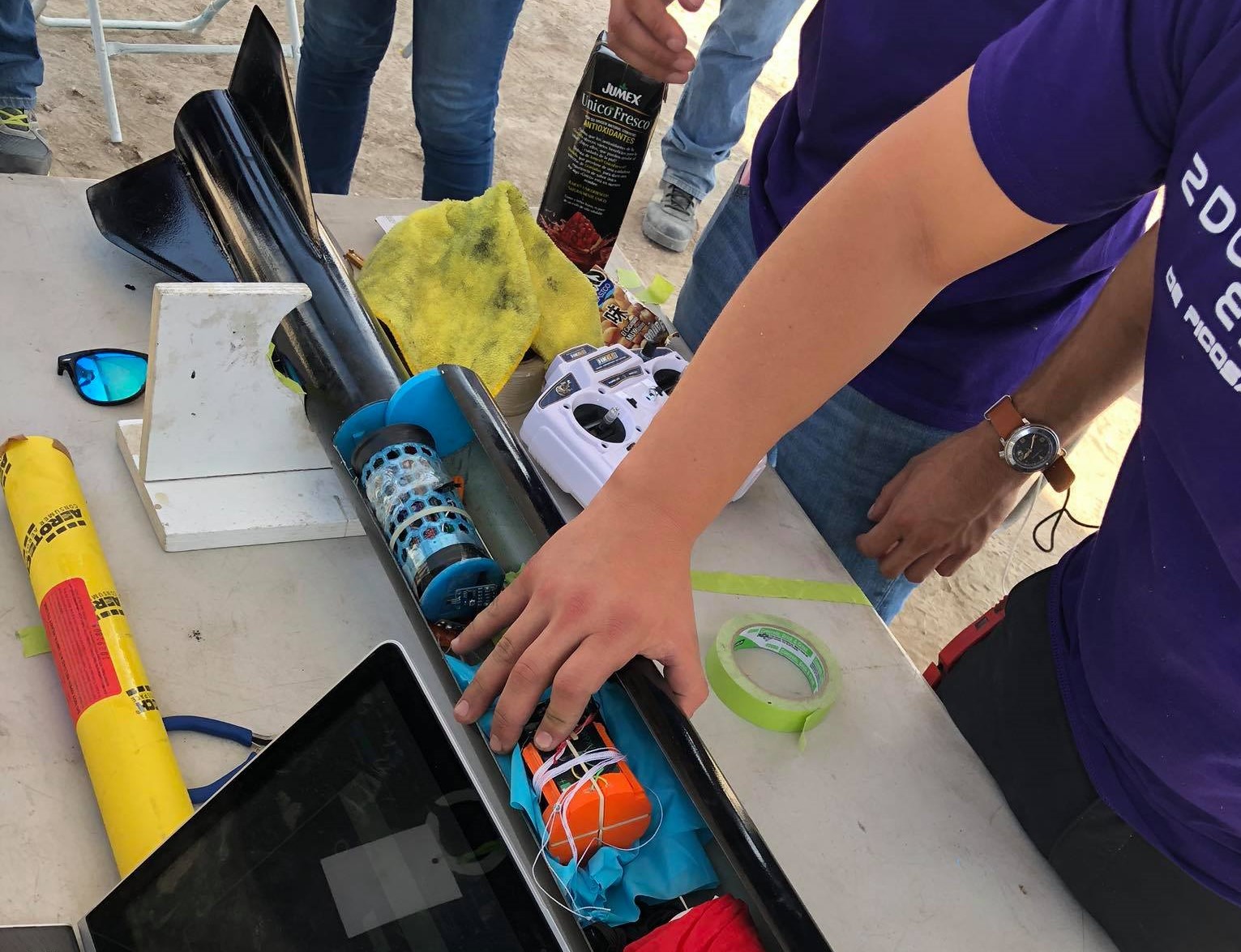

Implementation
The implementation of the CanSat was successful and cost effective with a fix cost of 70 dlls allowing for future scalability and easy to manufacture locally. A future improvement can be the development of surface mount components and a better microcontroller for more accurate ADC conversion.
